In Malaya also as in other colonies local negotiations of value systems and the accommodation and suppression of prostitution under colonialism. Of Colonial Sciences on Land Demarcation in Japanese Taiwan and British Malaya YEH ER-JIAN How to cite.

The Penang Bookshelf British Malaya An Economic Analysis Li Dun Jen
The post colonial Malaya inherited the colonial legacy in terms of a multi-ethnic society the federal.

Colonial land policy in british malaya. This article is a version of a paper given at the 9th Conference of the International Association of Historians of Asia in Manila Philippines November 1983. YEH ER-JIAN 2011 errTitorialising Colonial Environments. A Comparison of Colonial Scienesc on Land Demarationc in Japanese aTiwan and British Malaya Durham theses Durham University ailvAable.
The sample is dominated by investments in two key sectors of the colonial economy of British Malaya. Independence saw a change from the colonial language in favour of Bahasa Malaysia. In the 1890s the colonial regime had taken over the control of all matters related to land alienation in Malaya Tajud- din 2012 38.
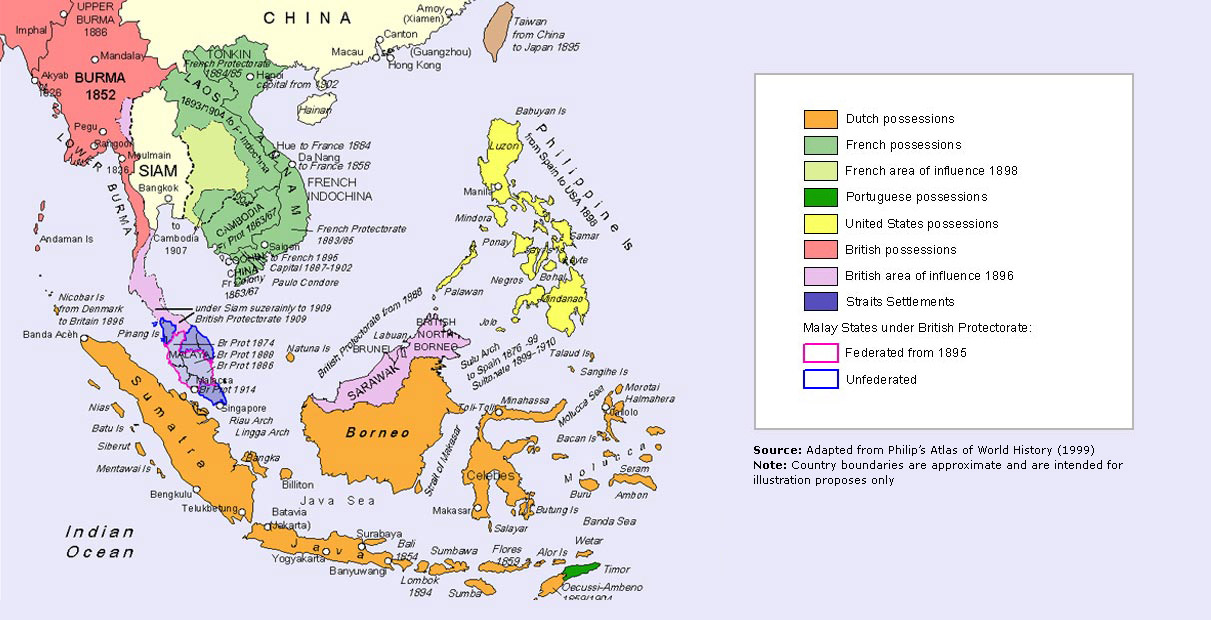
Meanwhile Singapore was acquired in 1819. The British colonial influence was profound because it established the institutions and policies on which the later ruling regime was based. Malaya under British administration which progressively spread over the Malay peninsula after the Pangkor treaty of 1874 was characterized by huge inequalities in wages and standards of living.
In British Malaya the colonial policies were responsible for the emergence of economic dualism characterised by a small prosperous European enclave sector dominated by large-scale plantations and tin-mining co-existing with a large native subsistence sector. In the form of land alienation policies. For many British anthropologists and colonial scholar-administrators the creation of knowledge surrounding indigenous peoples was based on efforts to catalogue and organise people and more importantly to give legitimacy to a colonial government in Malaya to claim unused jungle area for land development.
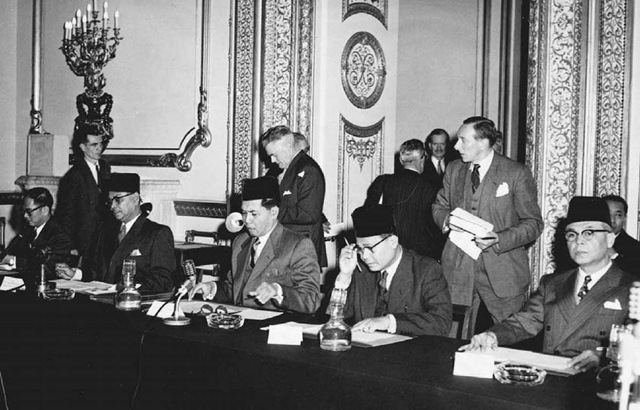
British imperial policy and decolonization in Malaya 194252. The pro-Malay aspect of British decolonisation as analysed by. The fourth phase of foreign influence was an immigration of Chinese and Indian workers to meet the needs created by the colonial economy in the Malay Peninsula and Borneo.
From the Revd Dr G. Request PDF TAXATION POLICY AND LAND REFORMS IN COLONIAL MALAYA During the 18th-19th centuries British influence started to change the situation of the economy and the society of Malaya as a. 30 These pockets of land were created not only to protect Malay settlements from land speculation and the growing rubber industry but also.
Resistance Protest in Colonial Malaya By Syed Muhd Khairudin Aljunied Northern Illinois University Press NUI 2015 228 pages On a night in 2010 a crowd of onlookers gathered to watch the demolition of a 300 metre wall of the century-old Purdu prison in Kuala Lumpur Malaysias capital. Japanese invasion during World War II ended British rule in Malaya. Chin Peng and British colonial policy in post-war Malaya.
Malacca was first occupied by the British from 1795 to 1818 and was formally ceded by the Dutch in 1825. This is important to understand the earlier political development in Malaya now known as Malaysia. The British economy itself was unable to accumulate US dollars because of the damage done to it by warfare but also because Britains ability to sell goods to the United States had been diminishing for 50 years.
I wish to acknowledge the support of the British Institute in South East Asia which enabled me to attend. English Approximately 60 of Malaysians speak English proficiently. Economic dualism was created not according to some grand de.
Disparities in colonial economic development are evidenced by the large differences in expenditure among different population groups. The plural policies of the British colonial rule had an adverse impact of Malaysia today as argued by historian Cheah Boon Kheng. In 1786 the sultan of Kedah granted the island of Penang to the British East India Company.
Sir Trevor Grundys review of Alias Chin Pengs My Side of History. Malaya was the Areas largest net dollar earner earning more than the rest of the other members of the Area put together. Beginning with the passing of the Malay Reservations Enactment in 1913 the colonial government set aside vast tracts of public land in both the FMS and UFMS for the exclusive use of and ownership by Malay people.
In British Malaya the circumstances were those of colonial capitalism built on the basis of imported male labor and the greedy demands for raw materials of industrializing Europe. This was at a time when. English was taught in schools and used in business and administration until 1956.
Based on extensive original research and including detailed case studies of the agricultural and mining sectors in late nineteenth and early twentieth century Malaya the book examines how. Here are eleven ways British colonialism transformed the nation and left a lasting legacy on Malaysian culture. TAXATION POLICY AND LAND REFORMS IN COLONIAL MALAYA inproceedingsGaniyev2020TAXATIONPA titleTAXATION POLICY AND LAND REFORMS IN COLONIAL MALAYA authorA.
Until 1867 it was known to the British as Prince of Wales Island. Colonial rule in Malaya.

Spaces Of Occupation Colonial Enclosure And Confinement In British Malaya Sciencedirect

Spaces Of Occupation Colonial Enclosure And Confinement In British Malaya Sciencedirect

Malaya Administrative Units Under British Colonization Download Scientific Diagram

Spaces Of Occupation Colonial Enclosure And Confinement In British Malaya Sciencedirect